

Therapy-Related Factors
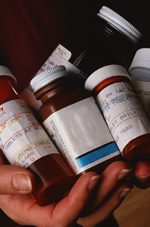 The complexity of the medication regimen, which includes the number of medications and number of daily doses required; duration of therapy; therapies that are inconvenient or interfere with a person's lifestyle (Krueger et al., 2003); and medications with a social stigma attached to its use (Tabor and Lopez, 2004) have been associated with decreased adherence.
The complexity of the medication regimen, which includes the number of medications and number of daily doses required; duration of therapy; therapies that are inconvenient or interfere with a person's lifestyle (Krueger et al., 2003); and medications with a social stigma attached to its use (Tabor and Lopez, 2004) have been associated with decreased adherence.
When medications such as antidepressants, are slow to produce effects, the older person may believe the medication is not working and may stop taking it (Tabor and Lopez, 2004). If administration of a medication requires the mastery of specific techniques, as with injections and inhalers, adherence may also be affected. Medication side effects can decrease adherence if patients believe they cannot control or manage them (Krueger et al., 2005).
| BARRIER | STRATEGIES |
|
Complexity of medication regimen (number of daily doses; number of concurrent medications)
|
Identify and discontinue unnecessary medications
Reduce dose frequency for medications where possible; use long-acting dosage forms where possible
Identify combination medications that can replace two separate prescriptions
Identify opportunities to use one drug to treat more than one medical condition
Identify medications prescribed to treat the side effects of other medications
Introduce reminder strategies tailored to the individual, such as pill organizers, calendars, phone reminder systems, etc.
Provide updated written list of medications
|
|
Lack of immediate benefit of therapy
|
Educate about what to expect from treatment (e.g., how medication works, time to onset of effect, expected goals of therapy, how to monitor for effectiveness)
|
|
Chronic or long-term therapy
|
Simplify regimen
Refer to support group
Use reminder strategies
Involve family members
Cue medication taking to daily tasks or routine
|
|
Actual or perceived unpleasant side effects
|
Educate about what to expect from treatment and risks vs. benefits (e.g., tolerance might develop to certain side effects)
Suggest ways to manage minor side effects
Identify alternative medications with less side effect potential
|
|
General treatment regimen concerns
|
Explore preferences and issues with treatment regimen:
Involve person in determining goals of therapy
Address medication-related issues that make adherence difficult, such as the need to master specific administration techniques (e.g., injections, inhalers)
|

